The GI of food is a classification based on the immediate effect of food on blood sugar levels. In other words: the speed at which carbohydrates from food are digested as glucose (sugar) in the blood.Read more about GI in this article.
Carbohydrates are the generic term for sugars, starch, fibres, …
Do we need carbohydrates and sugars?
Carbohydrates (e.g. sugars) provide energy; our brain works mainly on glucose (sugars). A constant supply of sugar is of such great importance for our brain and for any exercise we perform, that our body forms sugar reserves (glycogen). If the body finds too limited supply of sugars, it will break down muscle to generate them (ketones).Read about what happens when we eat too little sugar in this article.
Today, diabetics are allowed to eat more types of food than in the past, but a balanced and healthy diet remains very important. Coconut blossom sugar(organic coconut sugar)contains mainly slow sugars and may be included in a healthy diet that also contains other carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, minerals and healthy fats.Read more about coconut blossom sugar and diabetics in this article.

What is glycemic index (GI)?
The GI of food is a classification based on the immediate effect of food on blood sugar levels. In other words: the speed at which carbohydrates from food are digested as glucose (sugar) in the blood.
GI does not tell us how many carbohydrates are in our food, it tells us at which speed they are digested. Food containing carbohydrates (e.g. sugars) that quickly break down during digestion contain a high GI level. Food containing carbohydrates (e.g. sugars) that break down slowly and gradually release glucose (sugars) into our circulation have a low GI level. The speed at which carbohydrates (e.g. sugars) are digested in the mouth-stomach-intestinal canal has important consequences for diabetics, athletes, as well as on obesity and mood and vitality swings during the day. Designed in 1981 by Dr. David Jenkins, professor of nutrition of the University of Toronto, GI was a tool to determine which nutrients are most suitable for diabetics.
What are carbohydrates and sugars?
Carbohydrates are the generic term for sugars, starch, fibres, … The brain lives on glucose sugar. Our glycogen reserves are made from glucose sugar, a single sugar present in food in several carbohydrates from which it must be digested. Depending on the food type, this can occur quickly or slowly. The glucose hence enters the blood stream either quickly or slowly, and thus supplies energy rapidly (high GI) or at a more gradual pace (low GI).
Children and adults suffering from “dips”, obese people who want to lose weight and diabetics must choose for low GI food.
Depending on the situation, athletes can benefit from carbohydrates with both high and low GI levels. Endurance athletes benefit from carbohydrates supplying a low GI and strength athletes and short and fast movement athletes will profit from carbohydrates with high GI levels. After sports, carbohydrates with low and high GI levels are recommended for recovery of energy and muscle tissue.
Do we need carbohydrates and sugars?
Carbohydrates (e.g. sugars) provide energy; our brain works mainly on glucose (sugars). A constant supply of sugar is of such great importance for our brain and for any exercise we perform, that our body forms sugar reserves (glycogen). If the body finds too limited supply of sugars, it will break down muscle to generate them (ketones).
Who performed the coconut blossom sugar (organic coconut sugar) test?
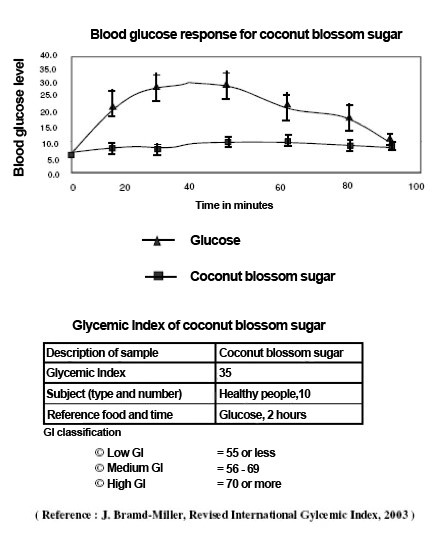
The Philippine Food and Nutrition Research Institute has discovered that coconut blossom sugar has a low GI of 35. Using coconut blossom sugar (organic coconut sugar) from the Cocos Nucifera, the test was performed on 10 people.
How was the GI of coconut blossom sugar established at only 35?

- Testees were administered 50g coconut blossom sugar carbohydrates.
- Blood samples were taken during the following two hours: every 15 minutes during the first hour and every 30 minutes by means of a finger prick (Vacutainer*) after that.
- The blood sugar levels were indicated in a graph.
- The curve was compared to the response curve and values for 50g glucose.
- The test was performed on 10 testees; the average outcome determined the GI level
*The serum was subsequently separated from the blood in a cooled Effendorf centrifuge, and that same day the glucose level was measured with the help of a Clinical chemistry analyser and after calibration of the glucose standard (Glucofix Reagent1 of Manarini Diagnostics).
GI and nice-to-know details
- Fat in food or meal lowers GI levels.
- Starch (e.g. French bread) contains more glucose molecules than sucrose (ordinary sugar).
- GI levels increase as a result of food processing or refining.
- Fibres lower GI levels.
- Food with high GI are mashed potatoes (GI 70), French fries (GI 75), French bread (GI 95), gluten free bread (GI 90), water melon (GI 72), raisins (GI 65), couscous (GI 65), vanilla wafers and dry biscuits (GI 77), cornflakes (GI 85), boiled sweet potatoes (GI 97), boiled pumpkin (GI75), sports drinks (GI 70 – 80), white sugar (GI 65), dried dates (GI 95), grape sugar/dextrose/glucose (GI 100 and serves as reference value).
- Low GI is value under 55, medium GI is between 56 and 69, high GI is over 70.
- 100% coconut blossom sugar has a low GI of 35. Attention: some palm sugars and coconut blossom sugars are mixed with cane or maltose sugars; although this softens the flavour and makes it cheaper, it also increases GI levels considerably!
Are diabetics allowed to eat coconut blossom sugar?
Today, diabetics are allowed to eat more types of food than in the past, but a balanced and healthy diet remains very important. Coconut blossom sugar(organic coconut sugar)contains mainly slow sugars and may be included in a healthy diet that also contains other carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, minerals and healthy fats. Many associations for diabetics recommend foods with low GI levels. The nutritious value of coconut blossom sugar can be found on the packaging and on this website. On top, coconut blossom sugar is rich in antioxidants, thus helping diabetics in their fight against free radicals. Amanprana coconut blossom sugar(organic coconut sugar)is lactose-free, cholesterol-free, gluten-free and does not contain allergens listed on the EFSA list.